| [1]Blagojevic M, Jinks C, Jeffery A, et al. Risk factors for onset of osteoarthritis of the knee in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18(1):24-33.[2]Heijink A, Gomoll AH, Madry H, et al. Biomechanical considerations in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis of the knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(3):423-435.[3]Liu XM,Xiang YC,Sun Q,et al. Zhongguo Bingli Shengli Zazhi. 2012; 28(2):362-365,370.刘兴漠,项禹诚,孙青,等.周期性张应力对骨性关节炎软骨细胞p38 MAPK表达及其磷酸化的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2012, 28(2):362-365,370.[4]Wang XQ,Li QH. Guowai Yixue:Shengwu Yixue Gongcheng Fence. 1999;22(2): 100-103.王序全,李起鸿. 机械应力异常与关节软骨退变[J]. 国外医学:生物医学工程分册,1999,22(2): 100-103.[5]Dou XL,Duan XQ,Xia L,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(20):3763-3766.窦晓丽,段晓琴,夏玲,等. 骨关节炎:关节软骨退变的相关研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(20):3763- 3766.[6]Zhai Y,Gao GD,Xu SY. Zhongguo Gushang. 2012;25(1): 83-87.翟云,高根德,徐守宇.膝关节骨关节炎的基础研究进展[J].中国骨伤,2012,25(1): 83-87.[7]Felson DT, Neogi T. Osteoarthritis: is it a disease of cartilage or of bone. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(2):341-344.[8]Mansell JP, Bailey AJ. Abnormal cancellous bone collagen metabolism in osteoarthritis. J Clin Invest. 1998;101(8): 1596-1603.[9]Zhang R, Fang H, Chen Y, et al. Gene expression analyses of subchondral bone in early experimental osteoarthritis by microarray. PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32356.[10]Zhang RK,Fang H,Lu HD,et al. Zhongguo Bingli Shengli Zazhi. 2011; 27 (12):2391-2395.张荣凯,方航,卢华定,等. Mmp3在早期骨关节炎模型软骨下骨的表达及其意义[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2011, 27 (12):2391-2395.[11]Takeshita S, Kikuno R, Tezuka K, et al. Osteoblast-specific factor 2: cloning of a putative bone adhesion protein with homology with the insect protein fasciclin I. Biochem J. 1993; 294 ( Pt 1):271-278.[12]Horiuchi K, Amizuka N, Takeshita S, et al. Identification and characterization of a novel protein, periostin, with restricted expression to periosteum and periodontal ligament and increased expression by transforming growth factor beta. J Bone Miner Res. 1999;14(7):1239-1249.[13]Ma D, Zhang R, Sun Y, et al. A novel role of periostin in postnatal tooth formation and mineralization. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(6):4302-4309.[14]Lindner V, Wang Q, Conley BA, et al. Vascular injury induces expression of periostin: implications for vascular cell differentiation and migration. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 200525(1):77-83.[15]Gillan L, Matei D, Fishman DA, et al. Periostin secreted by epithelial ovarian carcinoma is a ligand for alpha(V)beta(3) and alpha(V)beta(5) integrins and promotes cell motility. Cancer Res. 2002;62(18):5358-5364.[16]Bao S, Ouyang G, Bai X, et al. Periostin potently promotes metastatic growth of colon cancer by augmenting cell survival via the Akt/PKB pathway. Cancer Cell. 2004;5(4): 329-339.[17]Roy S, Patel D, Khanna S, et al. Transcriptome-wide analysis of blood vessels laser captured from human skin and chronic wound-edge tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(36): 14472-14477.[18]Malanchi I, Santamaria-Martínez A, Susanto E,et al. Interactions between cancer stem cells and their niche govern metastatic colonization. Nature. 2011;481(7379):85-89.[19]Hakuno D, Kimura N, Yoshioka M, et al. Periostin advances atherosclerotic and rheumatic cardiac valve degeneration by inducing angiogenesis and MMP production in humans and rodents. J Clin Invest. 2010;120(7):2292-2306.[20]Hopwood B, Tsykin A, Findlay DM, et al. Microarray gene expression profiling of osteoarthritic bone suggests altered bone remodelling, WNT and transforming growth factor-beta/bone morphogenic protein signalling. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(5):R100.[21]Yang J,Shi CH. Nongken Yixue. 2009;31(5): 448-451.杨坚,史晨辉. MMPs及相关细胞因子在骨性关节炎中的研究进展[J].农垦医学,2009,31(5): 448-451.[22]Xue SH,Wang ZL,Yang HJ. Zhongguo Difangbing Fangzhi Zazhi. 2007; 22(6):420-423.薛森海,王治伦,杨浩杰.基质金属蛋白酶及细胞因子在骨关节炎发病机制中的研究[J].中国地方病防治杂志, 2007, 22(6): 420-423.[23]Song PF,Kan WB,Yuan Q,et al. Guangdong Yixue. 2011;32 (20): 2736-2738.宋朋飞,阚卫兵,袁琴,等.基质金属蛋白酶与骨关节炎的关系[J]. 广东医学,2011,32(20): 2736-2738.[24]Li SC,Bao J,Wang GX. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu Zazhi. 2012;16(13):2407-2410.李盛村,鲍捷,王国祥. Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号通路在骨关节炎发生过程中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究杂志, 2012,16(13): 2407-2410.[25]Huang JG,Zhang XL. Zhongguo Yundong Yixue Zazhi. 2010; 29(4): 490-493.黄金刚,张晓玲. Wnt信号与骨关节炎[J].中国运动医学杂志, 2010, 29(4): 490-493.[26]Wang ZY,Wang WY,Zhang L. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2009;17(23): 1800-1803.王哲彦,王文雅,张柳.骨性关节炎的发病机制及其与 Wnt/β-catenin 信号通路的关系[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2009,17(23): 1800-1803.[27]Hurson CJ, Butler JS, Keating DT,et al. Gene expression analysis in human osteoblasts exposed to dexamethasone identifies altered developmental pathways as putative drivers of osteoporosis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2007;8:12.[28]Church V, Nohno T, Linker C, et al.Wnt regulation of chondrocyte differentiation. J Cell Sci. 2002;115(Pt 24): 4809-4818.[29]Shea CM, Edgar CM, Einhorn TA, et al. BMP treatment of C3H10T1/2 mesenchymal stem cells induces both chondrogenesis and osteogenesis. J Cell Biochem. 2003; 90(6):1112-1127.[30]Wu Q, Zhu M, Rosier RN, et al. Beta-catenin, cartilage, and osteoarthritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1192:344-350.[31]Yuasa T, Otani T, Koike T, et al.Wnt/beta-catenin signaling stimulates matrix catabolic genes and activity in articular chondrocytes: its possible role in joint degeneration. Lab Invest. 2008;88(3):264-274.[32]Zhu M, Tang D, Wu Q, et al. Activation of beta-catenin signaling in articular chondrocytes leads to osteoarthritis-like phenotype in adult beta-catenin conditional activation mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2009;24(1):12-21.[33]Thomas RS, Clarke AR, Duance VC, et al. Effects of Wnt3A and mechanical load on cartilage chondrocyte homeostasis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(6):R203.[34]Wu Q, Zhang Y, Chen Q. Indian hedgehog is an essential component of mechanotransduction complex to stimulate chondrocyte proliferation. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(38): 35290-35296.[35]Ng TC, Chiu KW, Rabie AB, et al. Repeated mechanical loading enhances the expression of Indian hedgehog in condylar cartilage. Front Biosci. 2006;11:943-948.[36]Lin AC, Seeto BL, Bartoszko JM, et al. Modulating hedgehog signaling can attenuate the severity of osteoarthritis. Nat Med. 2009;15(12):1421-1425.[37]King JA, Marker PC, Seung KJ, et al. BMP5 and the molecular, skeletal, and soft-tissue alterations in short ear mice. Dev Biol. 1994;166(1):112-122. |
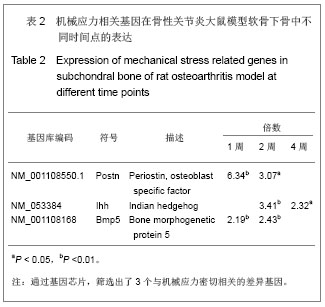
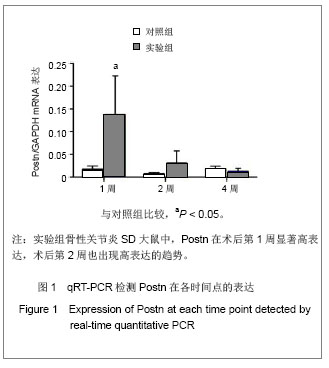
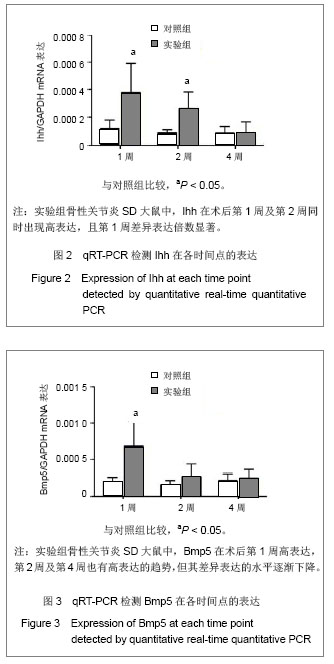
.jpg)
.jpg)